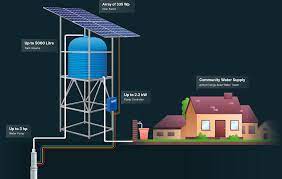
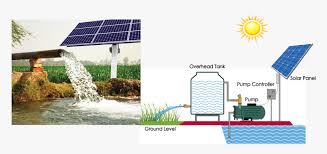
Solar panels have gained immense popularity as a renewable energy solution, promising not only a positive environmental impact but also potential savings on electricity bills. However, many homeowners and businesses still wonder: Do solar panels really save money? In this blog, we will dive deep into the financial aspects of solar panels and explore the tangible benefits they offer. We will debunk common myths, provide real-life examples, and unveil the long-term cost savings that can be achieved by embracing solar energy.
Exactly how much money solar panels can save you on your electricity bill varies from person to person and depends on several factors. Let’s take a closer look at why solar panels save money and how much cash they can keep in your wallet.
Key Points
· Solar panels can potentially save the average homeowner $130 per month on their electricity bills depending on where they live, their utility company, and their energy needs.
·Solar panels lower energy bills by generating electricity for your home to use, reducing the amount of power you need to buy from your utility company.
· With net metering and solar buyback programs, the electric company will purchase excess solar energy, which lowers electricity costs even more.
· Installing a solar power system costs between $12,600 and $14,000 including tax incentives.
How much does it cost to install a solar panel?
In 2021, the average cost of a solar panel installation was around $12,000 after the federal solar tax rebate. Smaller solar panel installations can cost as low as $5,000, whereas larger solar installations with the most advanced solar panels can cost upwards of $40,000 or more.
Can you get tax credits for solar panels?
Yes, the Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) was enacted in 2006, and in 2022 the ITC will be a 26 percent rebate. In 2023, the refund will be reduced to 22 percent.
Advantages Of Solar Panels-
Renewable Energy Source: Solar panels harness energy from the sun, which is a renewable and virtually limitless energy source. As long as the sun continues to shine, solar energy can be generated, reducing reliance on finite fossil fuels.
Environmentally Friendly: Solar panels produce clean energy without emitting harmful greenhouse gases or pollutants. Using solar energy helps combat climate change and reduces the carbon footprint associated with traditional energy sources.
Energy Cost Savings: Installing solar panels allows homeowners and businesses to generate their own electricity, reducing dependence on utility companies. This can lead to significant long-term cost savings on energy bills, especially as electricity rates continue to rise.
Financial Incentives: Many governments and local authorities offer financial incentives to promote the adoption of solar panels. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs, which provide additional financial benefits to solar panel owners.
Energy Independence: By producing their own electricity, individuals and businesses gain greater control over their energy supply. This provides energy security and reduces vulnerability to power outages or fluctuations in energy prices.
Disadvantages of Solar Panels:
High Initial Costs: The upfront cost of installing solar panels can be a significant barrier for some individuals and businesses. While the cost of solar panels has decreased in recent years, it still requires a substantial initial investment.
Weather Dependency: Solar panels depend on sunlight to generate electricity. Cloudy or rainy weather conditions can impact their efficiency and reduce energy production. However, solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, albeit at a lower output.
Space Requirements: Solar panels require adequate space for installation. Rooftop installations are common, but not all roofs may be suitable for solar panels due to orientation, shade, or structural limitations. Ground-mounted systems require available land space.
Maintenance and Repairs: Solar panels generally require minimal maintenance, but occasional cleaning, inspection, and repairs may be necessary. Accumulation of dirt, debris, or shading can affect performance, and repairs may incur additional costs.
Intermittent Energy Generation: Solar panels only produce electricity during daylight hours. This means that energy generation is intermittent, and supplemental energy sources or energy storage solutions may be needed for consistent power supply, especially during nighttime or cloudy periods.
Limited Efficiency: While solar panel efficiency has improved, not all sunlight is converted into usable electricity. Solar panel efficiency varies depending on factors such as panel quality, temperature, shading, and sun angle. Higher efficiency panels tend to be more expensive.